According to the wikipedia, diabetes mellitus, often known simply as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body becoming unresponsive to the hormone’s effects. Here you will find what is type 2 diabetes.
Useful Articles: 1. What is Diabetes? Basic Information. 2. Natural Treatment for Diabetes. 3. American Diabetes Association. 4. Treatment for Type 1 Diabetes. 5. What is Type 1 Diabetes?
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose).
Unlike type 1 diabetes, where the body doesn’t produce insulin, it occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels.
It is the most common form of diabetes, often linked to lifestyle factors.
Key Points about Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is largely influenced by lifestyle factors such as obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity, and genetics. Over time, these factors can lead to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells stop responding properly to insulin.
It typically develops in adults over 45 but is becoming increasingly common in younger people due to rising obesity rates.
Useful Articles: 1. Low Blood Sugar Symptoms: Daily Check Up. 2. Treatment for Gestational Diabetes. 3. Treatment For Diabetic Ketoacidosis. 4. Signs of Sugar Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms
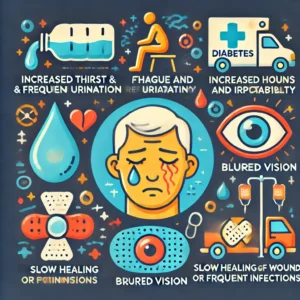
*Increased thirst and frequent urination.
*Fatigue and irritability.
*Blurred vision.
*Slow healing of wounds or frequent infections.
*Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight.
Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
Type 2 diabetes can often be managed with lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight. However, some people may need medications like metformin or insulin to help control blood sugar levels.
Complications
If not properly managed, it can lead to complications like heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems. It can also lead to more severe conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis (though this is more common in type 1 diabetes).

While it can be prevented or delayed through healthy lifestyle choices, it requires ongoing management to control blood sugar levels and prevent long-term complications.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a manageable condition with proper lifestyle choices and treatment.
It is often linked to factors such as obesity, poor diet, and lack of exercise, causing insulin resistance.
Symptoms like fatigue and frequent urination can be early signs.
With the right balance of medication, diet, and physical activity, blood sugar levels can be controlled effectively.
Awareness and early detection are key to preventing complications and maintaining a healthy life.









