Treatment For Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetes is continuously affecting the people around the world. By 2030 the diabetes would reach 643 million globally. There are 2 types of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Diabetic ketoacidosis is the next level of diabetes. In this article you will find full details of diabetic ketoacidosis and treatment for diabetic ketoacidosis.
Useful Articles: 1. What is Diabetes? Basic Information. 2. Natural Treatment for Diabetes. 3. American Diabetes Association. 4. Treatment for Type 1 Diabetes
How long does it take to die from diabetic ketoacidosis?
What are the warning signs of diabetic ketoacidosis? Diabetic ketoacidosis diagnosis, Diabetic ketoacidosis medication
How long does it take to recover from diabetic ketoacidosis?
What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious and potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes that occurs when the body starts breaking down fats at a rapid rate, producing ketones as a byproduct.
This typically happens when the body lacks enough insulin, which prevents glucose from entering cells for energy.
Instead, the body turns to fat for fuel, leading to the accumulation of acids called ketones in the blood.
Causes for Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
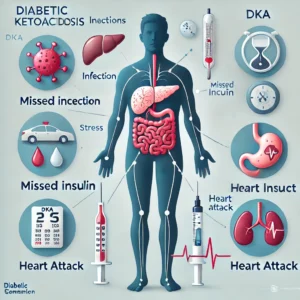
Insulin Deficiency: Common in people with type 1 diabetes but can occur in type 2 diabetes during severe illness or stress.
Infection, Illness, or Trauma: These can increase the body’s need for insulin, triggering DKA.
Missed Insulin Doses: Not taking prescribed insulin can also lead to DKA.
Useful Articles: 1. Signs of Sugar Diabetes. 2. Low Blood Sugar Symptoms: Daily Check Up. 3. Treatment for Gestational Diabetes
Symptoms For Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
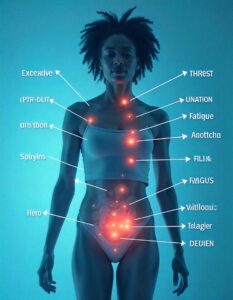
High Blood Sugar Levels: (above 250 mg/dL)
Fruity-smelling Breath: Caused by the buildup of ketones.
Frequent Urination and Thirst: The body tries to expel excess glucose.
Nausea, Vomiting, and Abdominal Pain
Fatigue, Confusion, or Unconsciousness
Rapid Breathing: Also called “Kussmaul respirations” (deep and labored breathing).
Treatment For Diabetic ketoacidosis
Insulin Therapy: To reduce blood sugar and stop fat breakdown.
Fluids and Electrolytes: To rehydrate the body and restore normal electrolyte levels.
Medical Monitoring: DKA requires hospitalization, as it can lead to complications like kidney failure or coma if untreated.
Preventing DKA involves regular blood sugar monitoring, following the prescribed insulin regimen, and taking action when blood sugar is high or ketones are detected in the urine.
Conclusion
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a severe complication that requires immediate attention.
Early recognition of symptoms such as fruity breath, nausea, and fatigue is crucial for timely intervention.
Treatment involves insulin therapy, rehydration, and electrolyte replacement to restore normal metabolic function.
With proper medical care, most patients recover fully.
Educating yourself and others about DKA can help prevent severe outcomes in the future.





